인류의 건강과 생명공학 발전을 위해 봉사하는 기업 드림셀
We Serving the Health and Biotechnology of Humanity
We Serving the Health and Biotechnology of Humanity

제품코드 : W6060
제품정보 : Inflammation Assay
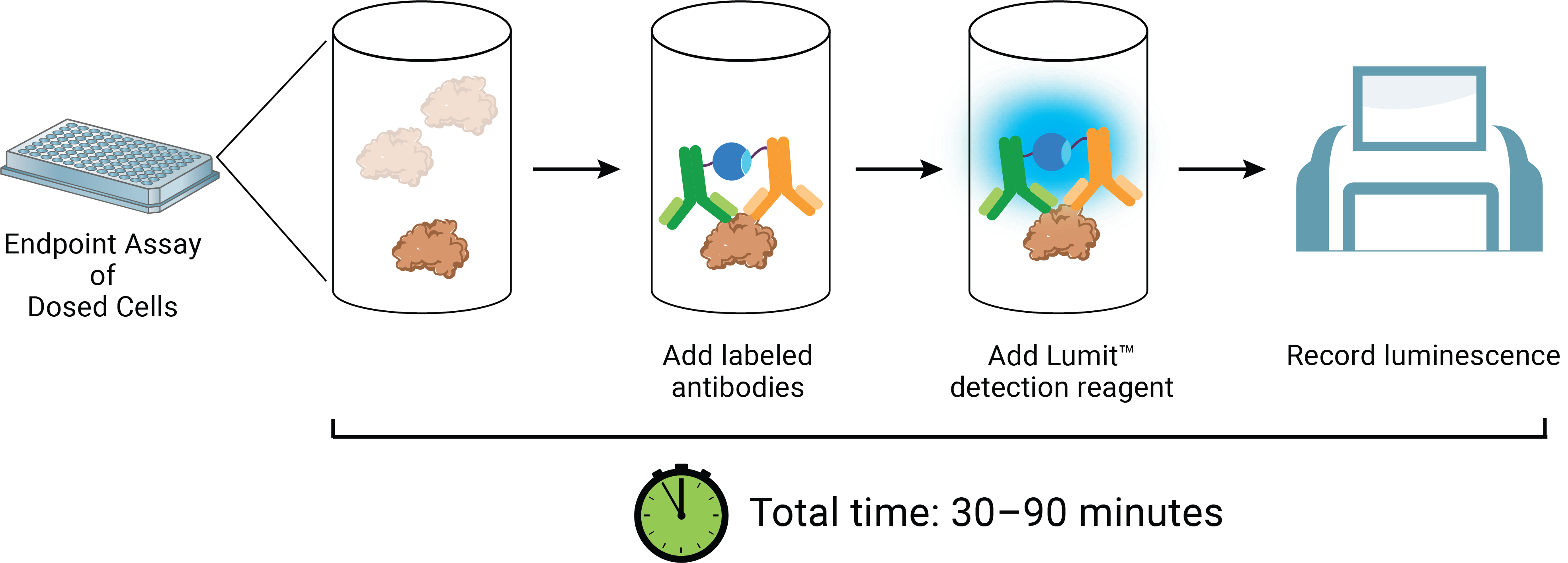
The Lumit™ IL-4 Immunoassay quantitatively measures released IL-4 in cell culture samples using a simple, no-wash protocol. Just add labeled antibodies to the sample, add detection reagent and read luminescent signal using a standard plate-reading luminometer. The entire protocol is completed in less than 70 minutes! The assay can be used directly on cells in culture or culture medium transferred to a separate assay plate.
Primary antibodies to IL-4 were selected for their specific and sensitive detection and labeled with the LgBiT and SmBiT subunits of NanoBiT® Luciferase. In the presence of IL-4, the subunits are brought together to form an active luciferase enzyme. Addition of optimized substrate generates a bright luminescent signal proportional to IL-4 levels.
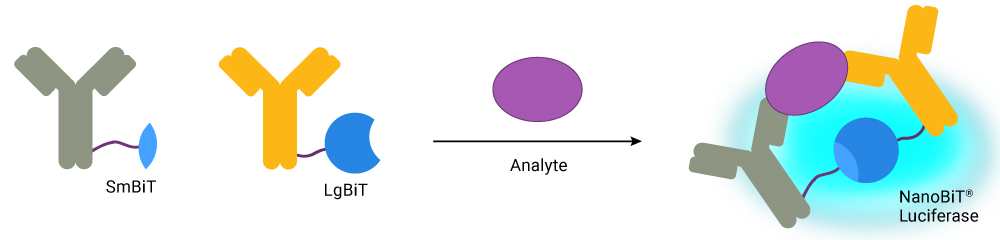

The pg/ml to ng/ml linear range of Lumit™ detection covers expected concentrations for most cell models.

Assay | IL-4 Human Immunoassay | |
Limit of Detection (LOD) | 6.7pg/ml (3 SD above background) | |
Dynamic Range | 18.2pg/ml – 25ng/ml | |
Minimal Detectable Dose (MDD) | 4.5pg/ml (2 SD above background) | |
Assay Time | 70 minutes | |
Sample Type | Cell culture supernatants | |
SD=Standard Deviation

When treated with a Cell Stimulation Cocktail (CSC), T helper type 2 (Th2) cells and human PBMCs (PBMC) each release low levels of IL-4. Following 24 hours of CSC treatment, Lumit™ IL-4 Immunoassay reagents were added directly to cell wells to measure IL-4 release.

Human T helper type 2 (Th2) cells were plated in 96-well plate format, primed overnight with hIL-2 and treated with increasing concentration of cell stimulation cocktail (CSC) for 24 hours. Following treatment, CellTox™ Green Cytotoxicity Assay and the Lumit™ IL-4 (Human) Immunoassay reagents were added to determine cytotoxicity and IL-4 release. CellTiter-Glo® Cell Viability Assay reagent was added to determine cell viability. A dose-dependent increase in IL-4 was observed, with some degree of increased cytotoxicity and decreased cell viability.